From August 2018 to now, the Standing Committee of the 13th National People’s Congress has divided and deliberated on the draft parts of the civil code. According to the codification work plan of the Civil Code, by December 2019, the General Principles of the Civil Code introduced in March 2017 will be merged with the sub-drafts of the Civil Code that have been reviewed and revised by the Standing Committee into a complete civil code, i.e., Civil Code of the People’s Republic (Draft). This is also the first overall appearance of the Civil Code .
Shen Chunyao, deputy chairman of the Constitutional and Legal Committee of the National People’s Congress, reported to the General Assembly on the amendments to the drafts of the Civil Code and the compilation of the Civil Code (Draft): “The Civil Code (Draft) consists of 7 chapters, which are in turn General Code, Property Rights, Contracts, Personality Rights, Marriage and Family, Succession, Tort Liability, and Bylaws, totaling 1260 Articles”.
(source: central network)
2020! Continue to review patent laws (revisions) and other bills
On the morning of December 20, the Legal Work Committee of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress held its third press conference. Yue Zhongming, the director of the Legislative Planning Office of the Legal Working Committee of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress, introduced the arrangements for the legislative work of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress in 2020 in response to questions from reporters.
Yue Zhongming said that the legislative work plan has been adopted in principle at the 44th Chairman’s Meeting of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress to make advance arrangements for next year’s legislative work.
Among them, an important task is that the draft civil code will be submitted to the Third Session of the Thirteenth National People’s Congress to be held on March for review. This is the first coded law in the history of New China.
Next year, the NPC Standing Committee will continue its consideration of Laws such as the Patent Law (modified), Solid Waste Pollution Prevention Law (modified), Archives Act (modified), Protection of Minors Act (modified), Prevention of Juvenile Delinquency Act (modified), the Public Service Disciplinary Action Act and the Biosafety Act.
(Source: Legal Person Learning Law)
Announcement on Amending the “Patent Examination Guidelines” (No. 343)
In order to fully implement the Party Central Committee and the State Council’s decision-making and deployment on strengthening intellectual property protection, and responding to the needs of innovation entities to further clarify the rules for examining patent applications in new formats and new fields such as artificial intelligence, it was decided to amend the Patent Examination Guidelines. It will be effective from February 1, 2020.
(Source: CNIPA)
The supreme law court revises the rules of evidence in civil litigation to clarify the rules of review and judgment on electronic data
Beijing, December 26 (Xinhua) The supreme law court held a press conference today to release the decision of the Supreme People’s Court on Amending the provisions on civil litigation evidence (hereinafter referred to as the “amendment decision”). The main contents of the “Amendment Decision” include the improvement of the recognitions of the parties and witnesses as well as appraiser commitment system, sanctions for false statements of parties and witnesses and false identification of appraiser, and promotion of the implementation of the principle of good faith in civil litigation; supplement and improve the provisions on the scope of electronic data, and clarify review and judgment rules of electronic data.
Changjiang Binxin, vice court of the Supreme People’s court, introduced that “several provisions of the Supreme People’s Court on evidence in civil proceedings” (hereinafter referred to as “provisions on Civil Evidence”) has been implemented since April 1, 2002. In 2015, the revision of the provisions on civil evidence was launched. It took four years to complete the revision of the provisions on civil evidence, which was discussed and adopted at the 1777th session of the judicial committee of the Supreme People’s court.
There are 115 articles in the revision decision, and 100 articles in the provisions on Civil Evidence re-published according to the revision decision. In the revised provisions on civil evidence, 11 of the original provisions on civil evidence have not been modified, 41 of the original provisions on civil evidence have been modified, and 47 provisions have been added.
(source: China News)
Printing and distributing the guide for administrative adjudication of patent infringement disputes
In order to implement the decision-making and deployment of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on strengthening the protection of intellectual property rights, effectively safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of innovators, patentees and the public, further strengthen the protection of patent rights, and improve the efficiency and level of administrative adjudication of patent infringement disputes, in accordance with the patent law of the people’s Republic of China, the detailed rules for the implementation of the patent law of the people’s Republic of China and the patent law of the people’s Republic of China, administrative law enforcement measures for patent and relevant laws and regulations, the guidelines for administrative adjudication of patent infringement disputes have been formulated; it is hereby printed and distributed for reference by all localities.
(source: The China National Intellectual Property Administration)
CPC Central Committee and State Council: establishing punitive compensation system for intellectual property infringement
On December 22, the website of the Chinese government released the opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on creating a better development environment to support the reform and development of private enterprises, which consists of eight parts and 28 articles. It is clear in the opinion that we should establish a punitive compensation system for intellectual property infringement and strengthen the protection of intellectual property. We need to improve evidence rules of intellectual property infringement litigation, as well as rules of evidence disclosure and evidence obstruction exclusion.
(source:daily)
Measures for the administration of intellectual property grants issued in Beijing
On December 9, Beijing Intellectual Property Bureau issued the administrative measures of Beijing Intellectual Property Fund (Trial) (hereinafter referred to as the administrative measures), which aims to encourage invention and creation, play out the leading role of brand, and improve the management level and use efficiency of intellectual property fund in Beijing.
According to the administrative measures, after the domestic invention patent application is allowed, each subsidy shall not exceed 1000 yuan. After the domestic design patent application is allowed, each subsidy shall not exceed 150 yuan. The annual amount of financial assistance provided by this article shall not exceed 2 million yuan.
According to the administrative measures, if an invention patent applied for through the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) is allowed in the United States, Japan or the European Patent Office, the subsidy for each patent in each country (region) shall not exceed 50,000 yuan; if it is allowed in other countries or regions, the subsidy of each country (region) shall not exceed 30,000 yuan. For invention patents applied for by other means than PCT, if they are allowed by the Patent Office of the United States, Japan or Europe, the subsidy for each patent in each country (region) shall not exceed 40,000 yuan; if it is allowed in other countries or regions, the subsidy of each country (region) shall not exceed 20,000 yuan. Each invention patent shall not be subsidized by more than 5 countries or regions. The total amount of the above-mentioned subsidy obtained by the applicant in the year shall not exceed 20 million yuan.
(source: V6 official website of Peking University Law)
5426 candidates passed the patent agent qualification examination in 2019
In August 2019, a total of 43,928 candidates for the patent agent qualification examination have passed the examination. The statistics is 11.65% higher than that in 2018, and the number of subjects registered has reached 118,000, a record high. The five regions with the highest growth rate are Fuzhou, Hefei, Shijiazhuang, Hohhot and Hangzhou.
From November 2 to 3, 2019, the patent agent qualification examination was successfully held in 30 cities across the country. Apart from Qinghai, Tibet and Ningxia, examination centers have been set up in four municipalities, 23 provinces and three autonomous regions. There are a total of 75 examination stations and 774 examination halls across the country, an increase of 57 compared with 2018.
In 2019, a total of 5,426 people passed the patent agent qualification examination and obtained the patent agent qualification certificate, with a passing rate of 12.35%. (Note: in 2018, 39,342 people signed up, 5,232 people passed the examination, with a passing rate of 13.3%)
(Source: Legal Person Learning Law)
Toyota China was fined more than 87.61 million yuan for monopoly
On December 27, the antimonopoly Bureau of the State Administration of market supervision and Administration issued the decision on administrative punishment of monopoly cases of Toyota (China) Investment Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as “Toyota China”). Toyota China was fined more than 87.61 million yuan by Jiangsu provincial market supervision administration and ordered to stop illegal activities due to price monopoly in sales of its Lexus brand cars.
It is confirmed that, upon authorization, the former price bureau of Jiangsu Province, in accordance with the anti-monopoly law, filed an investigation on Toyota China’s suspected price monopoly in the sales of Lexus brand cars in December 2017. In December 2019, the Jiangsu provincial market supervision administration made a decision on administrative penalty for the case.
It is found that Toyota China has the following illegal facts: (1) Toyota China has reached an agreement with dealers to limit the network quotation of dealers and the resale price of some vehicle models. (2) Toyota China has implemented an agreement to limit the dealer network quotation and the resale price of some vehicle models.
According to the market supervision and Administration Bureau of Jiangsu Province, the dealer is the trading counterpart of TOYOTA China, and the behavior of TOYOTA China to unify the dealer network quotation and limit the minimum price of resale goods belongs to the monopoly agreement reached and implemented with the trading counterpart that “fix the price of resale goods to the third party” and “limit the minimum price of resale goods to the third party”, which is in violation of Article 14 of the antimonopoly law.
According to the decision, Toyota China, with its own advantages and strict management measures, has a strong binding force on the unified network quotation made by dealers and the limit on the resale price of some models and complete vehicles. Toyota China’s actions exclude and restrict market competition and damage the interests of consumers.
Therefore, Jiangsu provincial market supervision administration decided to order Toyota China to stop the illegal act in accordance with the provisions of Article 46 and Article 49 of the antimonopoly law, and decided to impose a fine of 2% of the sales volume of the previous year (2016), i.e., 87,613,059.48 yuan.
According to the daily economic news, Toyota China has accepted the punishment on December 27: “because it is true, and we have corrected the relevant problems.”
(source: intellectual property power)
Dragon Special Report and Agency Practice
Make full use of divisional application strategy to protect your rights
I. Introduction
The divisional application system is stipulated in Rule 42 of the Implementing Regulations of the PRC Patent Law.
Furthermore, the Guidelines for Patent Examination (hereinafter, unless otherwise specified, refer to the revised Guidelines for Patent Examination implemented on November 1, 2019), part I, Chapter I, 5.1, etc. have detailed provisions on the divisional application system.
If used properly, the divisional application system can be a very favorable system.
II. Type and timing of divisional application
According to 5.1.1, Chapter 1, part I of the Guidelines, divisional applications can be divided into two categories: active divisional application and passive divisional application (divisional application based on OA issued by the examiner).
Further, 5.1.1 (3), Chapter 1, part I of the Guidelines stipulates timings of active division and passive divisional applications:
Active divisional application (including the two cases of actively filing a divisional application for a parent case and actively filing a divisional application for an already filed divisional application) does not require that there is a unity problem in the parent case; as long as the parent case is pending, divisional application can be filed anytime based on the parent case. In comparison, passive divisional application (divisional application (i.e., “second-generation divisional application”) re-submitted upon the examiner’s assertion of unity defect in a prior divisional application (i.e., “first-generation divisional application”)) is not subject to the timing of active divisional application; as long as the examiner points out the defect of unity and the first-generation divisional application is pending, even if the parent case is no longer pending, a divisional application can be filed.
In the following table, the author summarizes the timing of possible divisional applications according to the above regulations.
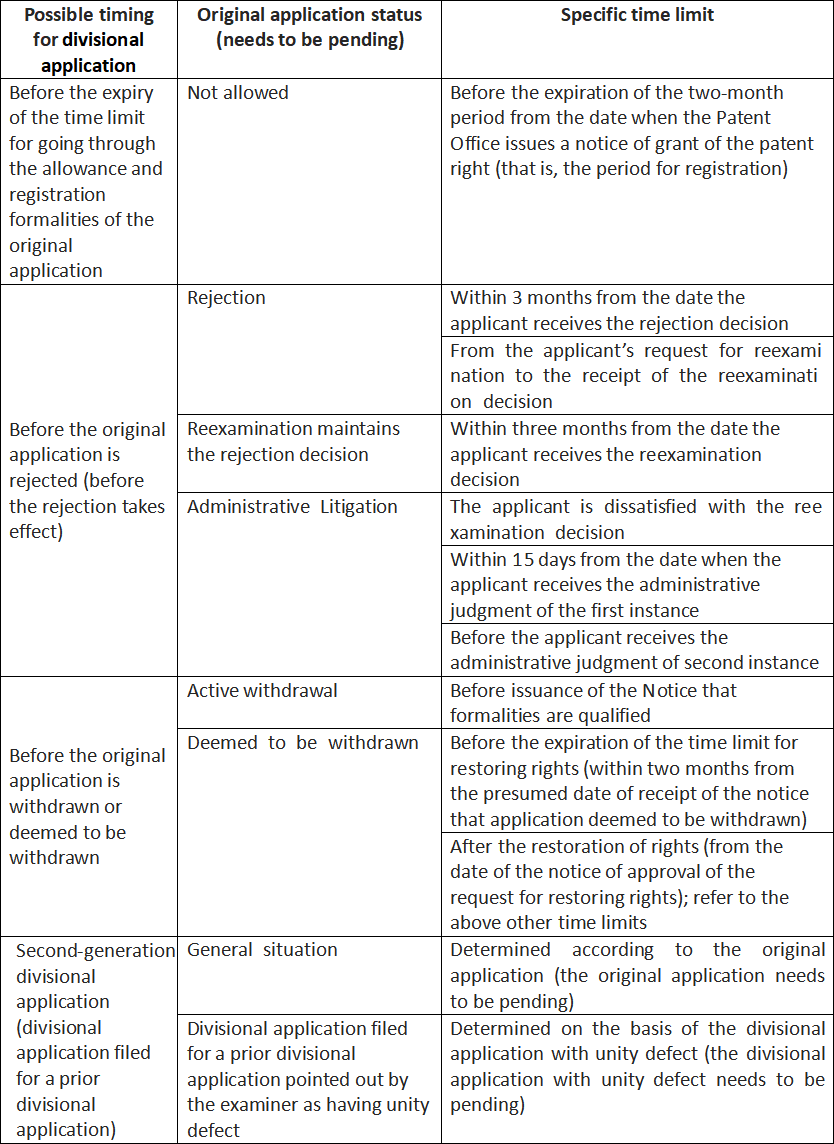
III. Make full use of the divisional application strategy to maximize the applicant’s rights
If we can make full use of the divisional application strategy, it is beneficial for striving for as much right as possible for the applicant and obtaining satisfactory results. The details are as follows.
1. Basic function
When a patent application is pointed out with unity defect, a divisional application may be submitted for claims and/or technical solutions that have to be deleted in order to overcome the unity defect.
2. Create opportunities for argument
If the applicant thinks that the reasons for the argument are sufficient, but the examiner or the collegial panel of the parent case insists that they are unacceptable, which results in the rejection of the parent case or uphold of the decision of rejection, the applicant may consider filing a divisional application. As a result, it is possible to continue to respond to the OAs of the divisional application, thus increasing the opportunity for success.
In some cases, examination of a patent application may coincide with the revision of the examination guidelines or the change of the examination policy. If such a change is favorable, it is advisable to postpone the examination process by means of filing extension, restoration or reexamination requests for the parent case, even filing administrative litigation against reexamination decision. It is also possible to further postpone the examination process, by using the time limits for divisional application mentioned in the table above, until implementation of the changed guidelines or policies. For example, in the current revision of the examination guidelines, “isolation or stem cell acquisition of human embryos within 14 days of fertilization without in vivo development” newly becomes subject matter that can be allowed a patent right; besides, GUI no longer requires combination with specifically applied products.
3. Starting from strategic considerations, protecting core products timely while striving to maximize the scope of protection
Generally speaking, the claims of a patent application are obtained by generalizing the core technical solution appropriately. On the other hand, in the examination of a patent application, all claims must be granted to obtain a patent right. In practice, there is often a dispute between the applicant and the examiner regarding the patentability of claims/technical schemes not involved in the core product. As a result, the case can be pending for a long while and its prospect for allowance is misty in short term. At the same time, the applicant’s core product is about to go on the market or involves other patent-related benefits. If the patent application is not granted as soon as possible, the listed product faces the risk of counterfeiting or damage of related interests. In this case, the disputed claims or technical solutions can be deleted first, so that the claims/technical solutions related to the core product can be granted as soon as possible. Then, a divisional application may be filed for the deleted claim/technical solution.
4. Avoid donation of technical solutions
In practice, a technical solution recited in the description and desirable to be protected may be neglected from being written in the claims and also not added to claims in proactive amendment. Besides, when responding to OA, technical solution in the original description cannot be drafted as a new claim. In such case, the neglected technical solution may be filed as a divisional application to avoid donation to the public due to its recitation in the description.
5. Confuse competitors
In the early stage of patent application, a technical solution likely to be infringed by competitors may be deliberately excluded from the claims but buried in the description. As a result, competitors may relax their vigilance because they can hardly retrieve the applicant’s patent in the early stage. Based on the applicant’s strategy, market situation and competitor’s situation, etc., the applicant may file such technical solution as a divisional application at the appropriate timing. Because competitors may only retrieve the granted claims of the parent case but fail to pay enough attention to those of the divisional application, their products may fall into the protection scope of the divisional application. Upon allowance, such divisional application will become a powerful weapon against competitors.
In addition, if there are multiple technical solutions in the description that are likely to cause infringement of competitors, the above strategy can be used to delay the examination process and make the parent case stay pending. Meanwhile, divisional applications are continuously filed. Because it is difficult for competitors to predict which technical solution in the description will be submitted as a divisional application next, competitors will be confused. In this way, technical solutions recited only in the description become weapons as powerful as those protected by granted claims.
6. Patent layout by N-generation divisional application
The strategies mentioned above are all based on active divisional application.
If the parent case cannot continue to be pending, one or more divisional applications with obvious unity defect may be filed before the parent case is closed. When the examiner of the divisional application points out the unity issue, a second-generation divisional application can then be filed based on the first-generation divisional application. This process can be conducted repeatedly. According to the current Implementing Regulations of the PRC Patent Law and guidelines for examination, if the second-generation divisional application is also pointed out as having unity issue and if the divisional application is in the pending state, a third divisional application can be filed based on the second-generation one. But it is necessary to take into account the risk that an examiner may not point out the unity issue, thus ending the possibility of a new divisional application. That is to say, this strategy cannot guarantee 100% success.
The non-exhaustive strategies are listed above for the applicants to refer to in practical operation. Applicants can take into account their own strategy, patent layout, competitors and other factors, and adopt appropriate divisional application strategy.
Finally, when submitting a divisional application, the applicant should also pay attention to some special provisions of the detailed rules in the Implementing Regulations of the PRC Patent Law and guidelines for examination, for example, the category of the divisional application shall be the same as that of the original application.
In addition, at present, the China National Intellectual Property Administration is very strict in monitoring abnormal applications. If the claims of a divisional application are identical with those of the parent application, it may very likely be determined as an abnormal application. Therefore, it is suggested that the claims of the divisional application be drafted as different from those of the parent case when submitting a divisional application, rather than submitting the divisional application with the same claims as the parent case first and then making proactive amendment.
(author: Weidong WANG, patent agent, lawyer of business research group)
Please feel free to contact us:
Tel: 0086-10-82252547
Fax: 0086-10-82250563
Email: marketing@dragonip.com
