The forum has a main forum and six special forums covering geographical indication protection, intellectual property examination quality and efficiency improvements, overseas intellectual property layout, artificial intelligence and intellectual property protection, trademark examination to promote brand economy, and sports industry intellectual property protection and other hot topics. Nearly 70 Chinese and foreign guests will give speeches around the theme of the forum, exchange ideas, build consensus, and jointly explore a new path to comprehensively strengthen intellectual property protection.
(Source: CNIPA website)
In 2018, the number of newly received intellectual property cases in the national courts exceeded 330,000, increasing 40% over the same period of last year.
In 2018, the number of first-instance cases involving intellectual property competitions (including monopoly civil cases) newly received by the local people's courts increased at the highest level, up 63.04% year-on-year. As the President of the Intellectual Property Tribunal of the Supreme People's Court, SONG Xiaoming, introduced, the number of cases received by the courts in Beijing, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Guangdong last year remained at a high level. The number of newly received first-instance IPR civil cases was 185,337, accounting for 65.39% of the first-instance IPR civil cases newly received by the national courts. In order to further optimize the jurisdictional pattern of intellectual property cases and integrate intellectual property trial resources, the Supreme People's Court approved in 2017 to establish specialized intellectual property institutions across jurisdictions in 11 cities including Nanjing and Suzhou. On this basis, it was approved in 2018 to establish intellectual property courts in eight cities including Tianjin, Zhengzhou, Changsha, Xi'an, Nanchang, Changchun, Lanzhou and Urumqi. At present, except that Lanzhou and Urumqi courts will be unveiled this year, the other six intellectual property courts have been unveiled and officially started.
(Source: People.cn)
Anti-counterfeiting cannot be "independent", and attention shall be paid to technological innovation and effectively protect intellectual property rights
The intellectual property protection system from China's digital economy is becoming a model on a global scale. At the "Global Luxury Law Alliance Summit" held recently, Chinese Internet company Alibaba was awarded the "Intellectual Property Protection and Technology Innovation Award". It is worth noting that some people who have expressed doubts about the online e-commerce fraud in China have now become their partners.
According to an earlier report by the Economic Voice, a report from a market research company shows that the total loss caused by global counterfeit goods in 2017 reached 1.2 trillion US dollars, and is expected to rise to 1.82 trillion US dollars by 2020. The total loss caused by the counterfeit goods sold online amounted to 323 billion US dollars. With the increasing globalization of counterfeit goods, the large-scale organization of the fake and black goods industry chain poses greater challenges to offline fraud. In addition, the methods, tools and techniques used by counterfeiters are also escalating, which puts new demands on regulation.
The chief platform administrator of Alibaba, ZHENG Junfang, believes that anti-counterfeiting cannot be “independent”. Any national government, enterprise, social organization and individual should actively participate in it, forming a grid-like pattern of global governance of counterfeit goods. Counterfeit goods are public nuisances. Any fake, fake sellers and "spoofing" without taking practical measures such as playing fakes and even condoning the cover-ups should become the public enemy of the whole society. Nowadays, anti-counterfeiting means is innovated relying on artificial intelligence technology, etc.
(Source: People.cn)
Foreign Investment Law: Helping Intellectual Property Protection and Technical Cooperation
On March 15, 2019, the Second Session of the 13th National People's Congress reviewed and approved the Foreign Investment Law. The Foreign Investment Law completely replaces the previous "three laws on foreign investment", namely, the Sino-foreign joint venture enterprise law, the foreign-funded enterprise law and the Sino-foreign cooperative enterprise law, establishing the basic framework of China's new foreign investment legal system, and is the new foundation for China's foreign investment. Intellectual property rights and technical cooperation in the foreign investment system have been always an important part of the foreign investment legal system. At the same time, both of the Sino-foreign joint venture enterprise law and the Chinese cooperative enterprise law regard intellectual property rights such as industrial property rights as important contents of investment, and the foreign-funded enterprise law regards “technically advanced foreign-funded enterprises” as the object of encouragement.
Provisions on intellectual property rights and technical cooperation during the legislation of foreign investment law have received much attention. First, in the process of deliberation of the National People's Congress, provisions on the protection of trade secrets have been added, so that the provisions on intellectual property protection have been enriched and improved. Second, in the process of deliberation of the National People's Congress, the protection of intellectual property rights will be further strengthened, the responsibility for intellectual property infringement will be strictly investigated, and the relevant expressions of “strictly investigate legal responsibilities for infringement of intellectual property rights” will be added. Third, the transfer of technical cooperation provisions from intellectual property protection provisions to technology transfer provisions is more in line with legal logic and practical needs.
The Foreign Investment Law will be implemented on January 1, 2020. It is believed that before this, there will be relevant implementation rules, administrative regulations and departmental regulations. Articles 20, 21 and 22 of the Foreign Investment Law put forward higher requirements for the compliance of intellectual property rights and technical cooperation, and need to be highly concerned in practice. Especially in the technical cooperation projects for foreign investment, the following three aspects need to be paid attention to.
First, prevent the compulsory transfer of technology in terms of technical cooperation, that is, the conditions for technical cooperation are determined by the investment parties in accordance with the principle of fairness, and the administrative organs and their staff members must not use administrative means to force the transfer of technology; second, pay attention to the protection of intellectual property rights in terms of contents of technical cooperation, that is, protect the intellectual property rights of foreign investors and foreign-invested enterprises, protect the legitimate rights and interests of intellectual property rights holders and related rights holders, and pursue legal liability for intellectual property infringements strictly in accordance with the law; third, guarantee the intellectual property license fees for foreign investors in China to be remitted freely in RMB or foreign exchange in accordance with the law in terms of technical cooperation income.
(Source: China Intellectual Property Network)
3D printing patent applications increased significantly
Recently, patent data company IPlytics has released 3D printing technology patent application and litigation trend report. According to the report, the number of patent applications for 3D printing technology is increasing rapidly, and the number of transfer and lawsuits of related patents are increasing as well.
According to the report, among the top 10 3D printing patent applicants in the world, except for Siemens in Germany, the rest of the applicants are from the United States. Among them, the General Electric Company ranked first, followed by Hewlett-Packard Company, United Technologies Corporation, Siemens Company, Boeing Company. One of the top 10 leading applicants is Harvard University. In addition, viewing from the geographical distribution of patents, the number of patent applications related to 3D printing accepted by the US Patent and Trademark Office topped the list, followed by the State Intellectual Property Office of China and the European Patent Office.
(Source: China Intellectual Property Information Website)
Dragon IP organized staff to participate in the event of the China National Intellectual Property Administration Open Day
On April 25, 2019, Dragon IP organized staff to participate in the Open Day event held by the China National Intellectual Property Administration. The theme of the Open Day this year is “Approaching Intellectual Property Rights”. The commissioner of the China National Intellectual Property Administration, SHEN Changyu, the deputy director general of the WIPO, WANG Binying, representatives of the intellectual property service industry, representatives of innovative enterprises, teachers and students of the IP Education Pilot Model School, media reporters and volunteers participated in this event.
By participating in this event, the staff of Dragon IP have a deeper understanding of the history of intellectual property development, are proud of their work in intellectual property service, and have strengthened their determination to contribute to the development of intellectual property.
Specials and Practice of Attorney
Analysis on the principle of "conformity with the purpose of invention" in claim explanation
Claims are the most important legal documents in a patent document that define the protection scope of an invention or utility model. In the actual authorization, confirmation and infringement procedures, claims often need to be interpreted in determining the protection scope of an invention or utility model. Therefore, the interpretation of the claims becomes an important part of the authorization, confirmation and infringement procedures.
The mainstream view of the industry is that the rules for the interpretation of claims in authorization, confirmation and infringement procedures are not identical completely. In addition, the application of principles of claim interpretation such as the principle of fairness, the principle of compromise, the principle of conformity with the purpose of invention and the principle of estoppel also largely determines the direction of the case. This article starts from two cases to discuss the application of the principle of “conformity with the purpose of invention” in the determination of confirmation and infringement procedures and propose some countermeasures in the process of authorization, confirmation and infringement.
I. Legal basis:
1. Paragraph 1, Article 59 of the PRC Patent Law
The protection scope of an invention or utility model patent is based on the contents of claims, and the specification and drawings can be used to explain the contents of the claims.
2. "4. The principle of conformity with the purpose of invention” in “(I) the principle of explanation for determining the protection scope” of “I. Determination of the protection scope of invention and utility model patents” as provided in “Guidelines for Determination of Patent Infringement (2017)” issued by the Beijing Higher People's Court on April 20, 2017
In the determination of the patent protection scope, the technical solutions that cannot achieve the object and effect of invention should not be construed into the protection scope of the claims, that is, those skilled in the art, on the basis of combining the technical background of the field, after reading the entire contents of the specification and drawings, still considers the technical solution which cannot solve the technical problem of the patent and realize the technical effect thereof shall be not construed into the protection scope of the patent.
II. Case analysis
1. Case 1
Claim 1 of the involved patent is directed to a camera assembly and defines "the lens portion is placed and fixed above the logic circuit portion of the image sensor chip".
In the process of invalidation, the petitioner believes that "fixed" should include two cases: "direct fixed" and "indirect fixed", but the patentee believes that the "fixed" here should be interpreted only as "direct fixed".
According to the description of the specification of the involved patent, the object of the invention is to "miniaturize" and to "improve focus accuracy".
★ Regarding "miniaturization"
It is described in the specification of the involved patent that the lens portion is directly placed and fixed on the image sensor chip, so that the camera assembly can be made smaller in size (including horizontal direction and height direction).
★ Regarding "improve focus accuracy"
The specification of the involved patent also recites that "the original camera assembly has a lens 101, two parts constituting a lens barrel 102, a substrate 104, a package 108 and an image sensor chip 106, etc due to the structure for determining the path length between the lens 101 and the image sensor chip 106. The dimensional errors in respective structures and the errors caused by the mutual connection thereof are superimposed. Therefore, the path length fluctuation between the lens 101 and the image sensor chip 106 is large, and the focus accuracy is low". Further, the specification also describes that, in the present invention, "as there is only a lens support portion between the lens and the image sensor chip, the cumulative error is small, and the relative positions of the two can be accurately fixed".
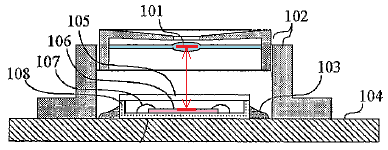 Fig. A (conventional components)
Fig. A (conventional components)
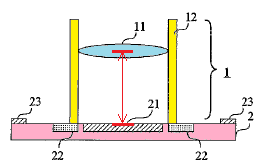 Fig. B (involved patent)
Fig. B (involved patent)
"Improving focus accuracy" refers to reducing the error (the distance indicated by the arrow in the above figure) caused on the path length between the lens and the image sensor chip. Thereby, distortion and blurring of the image can be suppressed to obtain a good image.
The error (the distance indicated by the arrow in the above figure) caused on the path length between the lens and the image sensor chip is the superposition of the dimensional errors of multiple components and the errors caused by the connection between the components. However, the involved patent has specified in the specification that there is only the lens support portion 12. This means that the lens support portion is placed "directly" on the image sensor, without incorporating other component, which is in line with the usual meaning of "placed" in the claims.
However, in the conventional assembly, the image pickup element is fixed to the wiring substrate, and the lens portion is also fixed to the wiring substrate, thereby forming a photographing assembly, which does not have the advantages of the above-mentioned involved patents.
It thus can be seen that, based on the invention object of the involved patent, indirect fixing cannot achieve the object of the invention (especially, the purpose of "improving the focus accuracy" cannot be achieved), therefore, ”the lens portion is placed and fixed above the logic circuit portion of the image sensor chip” in claim 1 shall not be explained to include the case of indirect fixing.
In the invalidation decision No. 33602 made by the Patent Reexamination Board, the patentee's point of view was supported and the patent right was maintained valid.
The petitioner of this case was not satisfied with the decision and filed an administrative lawsuit with the Beijing Intellectual Property Court, but withdrew the lawsuit before the judgment was made in this case.
2. Case 2
The basic circumstance of this case is: Jinli company is the patentee of the invention patent entitled “switch of loaded-regulating capacity regulating transformer in power grid of 20KV and below” (patent number ZL200910187320.1, hereinafter referred to as the involved patent), which believes the alleged infringing products manufactured and sold by Daosheng company have fallen within the protection scope of the claims in the involved patent, constitute infringement and therefore are appealed to the court, requesting to order the Daosheng company to immediately stop the infringement, compensate for economic losses and eliminate impact.
The focus of dispute in this case is whether the "multiple" in the technical feature "series multiple fractures" in claim 1 of the involved patent contains "double". Because the corresponding technical feature of the alleged infringing product is “series multiple fractures”, whether “multiple” contains “double” will directly affect whether the alleged infringing product falls within the protection scope of the involved patent.
In this regard, the second-instance court held that it is difficult to form a majority consensus on the abstract interpretation of whether “multiple” in Chinese can contain “double” from the existing Chinese dictionaries, reference books and the ordinary perception of people, and neither of the two parties put forward a good reason to convince the other party. However, in the technical field of the switch of loaded-regulating capacity involved in the present case, according to the invention object of the involved patent and in combination with the existing evidence, the “multiple” in the “series multiple fractures” of claim 1 in the involved patent should not contain “double”, therefore, the “series multiple fractures” used by the alleged infringing product and its technical solutions formed together with other technical features should not fall within the protection scope of the claims in the involved patent. The specific reasons are as follows.
First of all, according to the contents described in the specification of the involved patent, the technical feature of disposing series multiple fracture contacts on the high-voltage side aims to solve the technical problem of “reliable arc-extinguishing of contacts on the high-voltage side in the star-angle switching process”.
Secondly, in order to solve this technical problem, the involved invention reduces the switching voltage on a single contact by increasing the number of series fractures, thereby realizing "reliable arc-extinguishing of contacts on the high-voltage side in the star angle switching process".
Thirdly, according to the specification of the involved patent and the contents of relevant technical data, under normal circumstances, the switching ability of the single contact breakpoint of the loaded switch cannot be higher than 2000V. Only after special design, the switching ability of the single contact breakpoint can be made higher than 2000V. However, claim 1 in the involved patent does not specifically limit the structure of the main contacts and the transition contacts of the series multiple fractures, but only defines the connection manner of the contacts and the windings. Therefore, in the explanation of the claims, the series multiple fractures in claim 1 of the involved patent should be understood as a series multi-fracture structure in general cases, and the switching ability of the single contact breakpoint cannot exceed 2000V.
Fourth, the alleged infringing product is applied to the voltage environment of 10KV. According to the calculation method described in the specification of the involved patent, the switching voltage of the single contact breakpoint can be guaranteed to be lower than 2000V only when the number N of series fractures of the switch of loaded-regulating capacity is greater than 3. When N=2, the cut-off voltage of the single contact breakpoint is 2886.5V greater than 2000V, which cannot achieve the purpose of "reliable arc-extinguishing of contacts on the high-voltage side in the star angle switching process". Therefore, in the voltage environment of 10KV applied in the alleged infringing product in this case, the “series multiple fractures” in claim 1 of the involved patent cannot be interpreted to include “double”, and can be interpreted to be only three or more. "Series double fractures" adopted by the alleged infringing product cannot be included in the range of the "series multiple fractures" of the involved patent. They belong to different technical features.
In the Civil Judgment No. 00237 of Jiangsu High Court (2015), the second-instance court did not support the claim of the patentee.
III. Opinions and suggestions of attorney
According to the principle of conformity with the purpose of invention, in writing claims, the technical solutions of the claims should be objectively written in combination with the technical problems to be solved and the technical effects (i.e., the purpose of the invention) that can be achieved by the patent application, and the solution that cannot achieve the purpose of invention cannot be contained in the claims in order to pursue overbroad protection scope.
In confirmation and infringement procedures, when determining the meaning of the technical features in the claims, the meaning of the feature in the context of the specification shall be objectively determined based on the technical solutions defined by the claims and in combination with the technical problems solved and the technical effects (i.e., the purpose of invention) that can be achieved by the solutions, avoiding a simple and broad understanding of the technical features apart from the invention itself.
IV. Summary
This article introduces the relevant legal basis for the application of the principle of conformity with the object of invention. Furthermore, two cases from the Patent Reexamination Board were analyzed. The application of the principle of conformity with the object of invention in determining the protection scope of the claims was explained through these two cases. Finally, some countermeasures in the authorization, confirmation and infringement procedures are discussed in order to provide reference for the actual attorney work.
(Author: WANG Yonghui from Mechanical Department)
If you have any questions, please contact us by Tel: 0086-10-82252547, Fax: 0086-10-82250563, and Email: marketing@dragonip.com.
